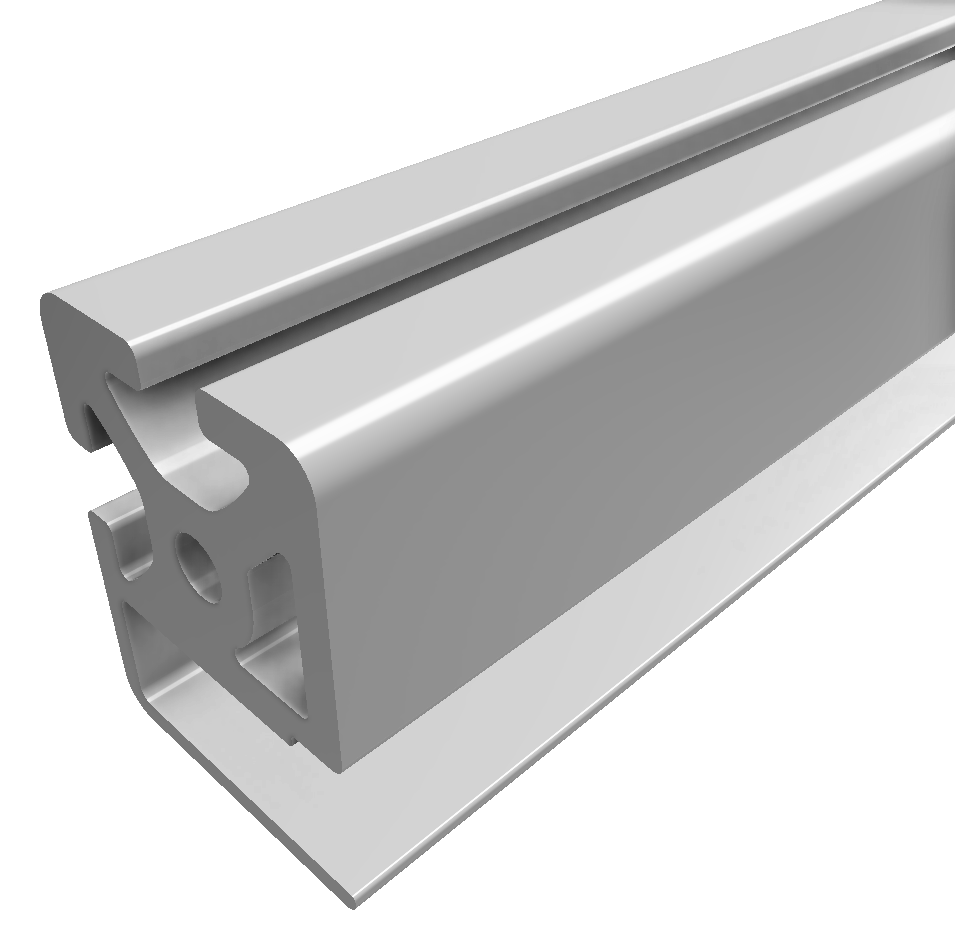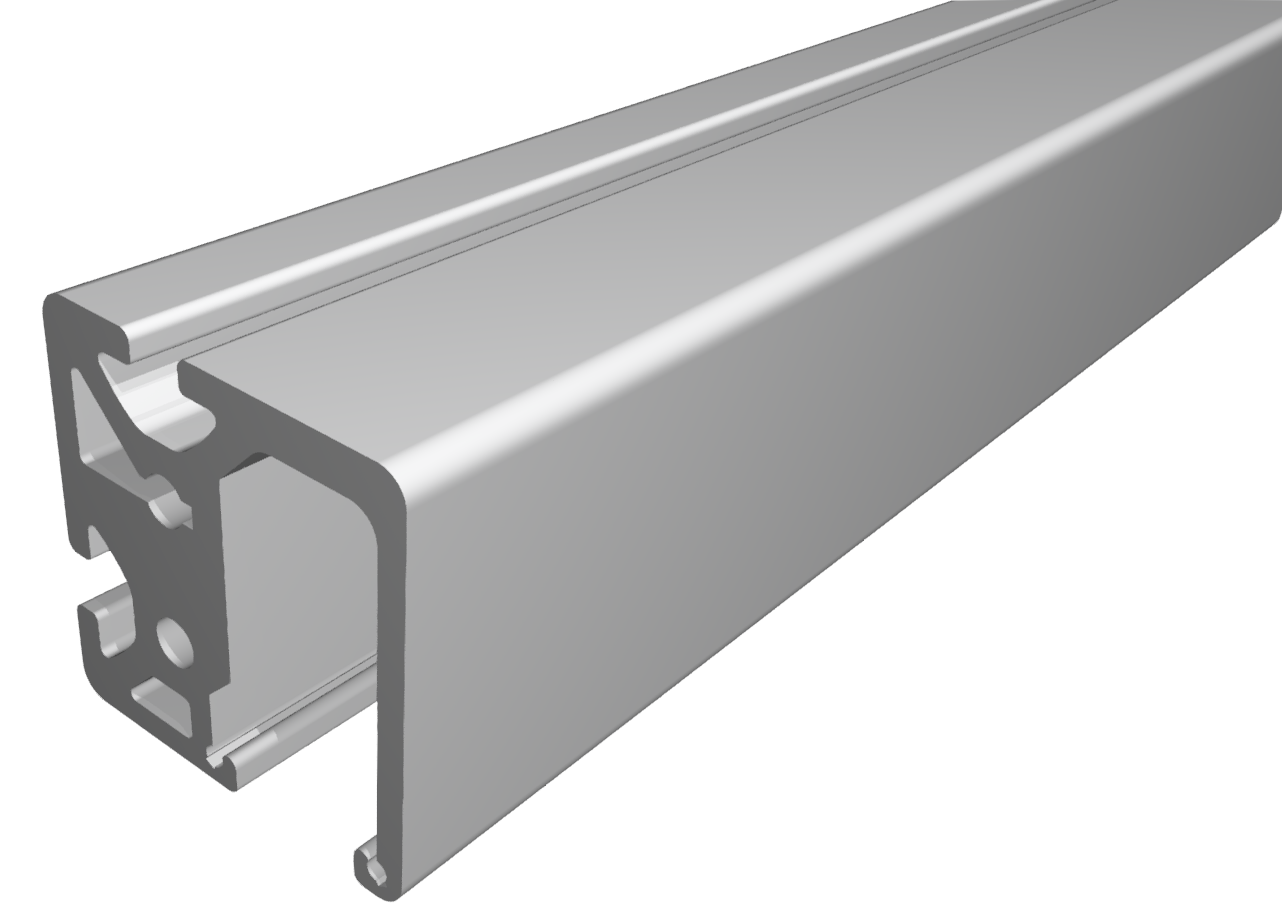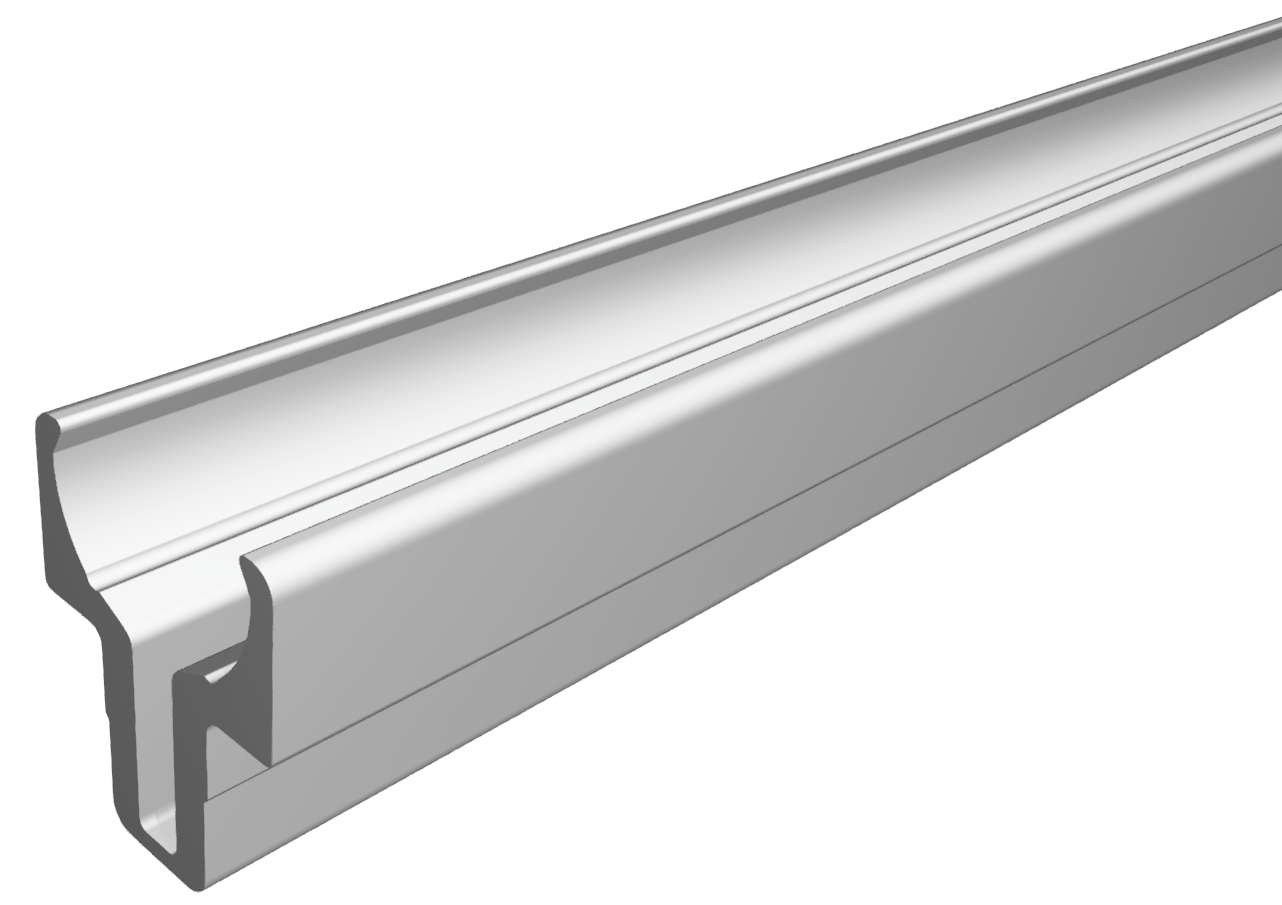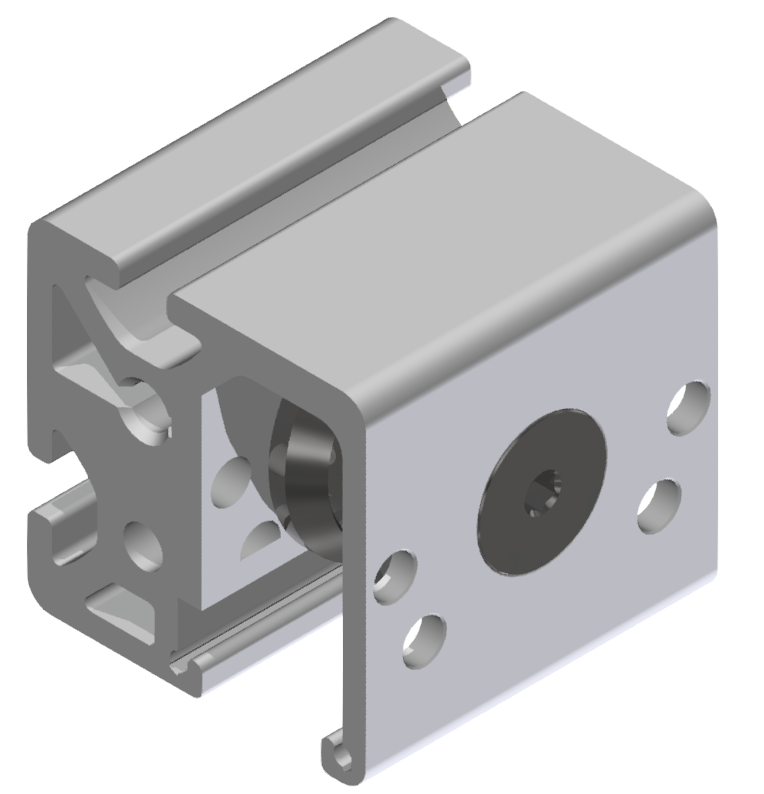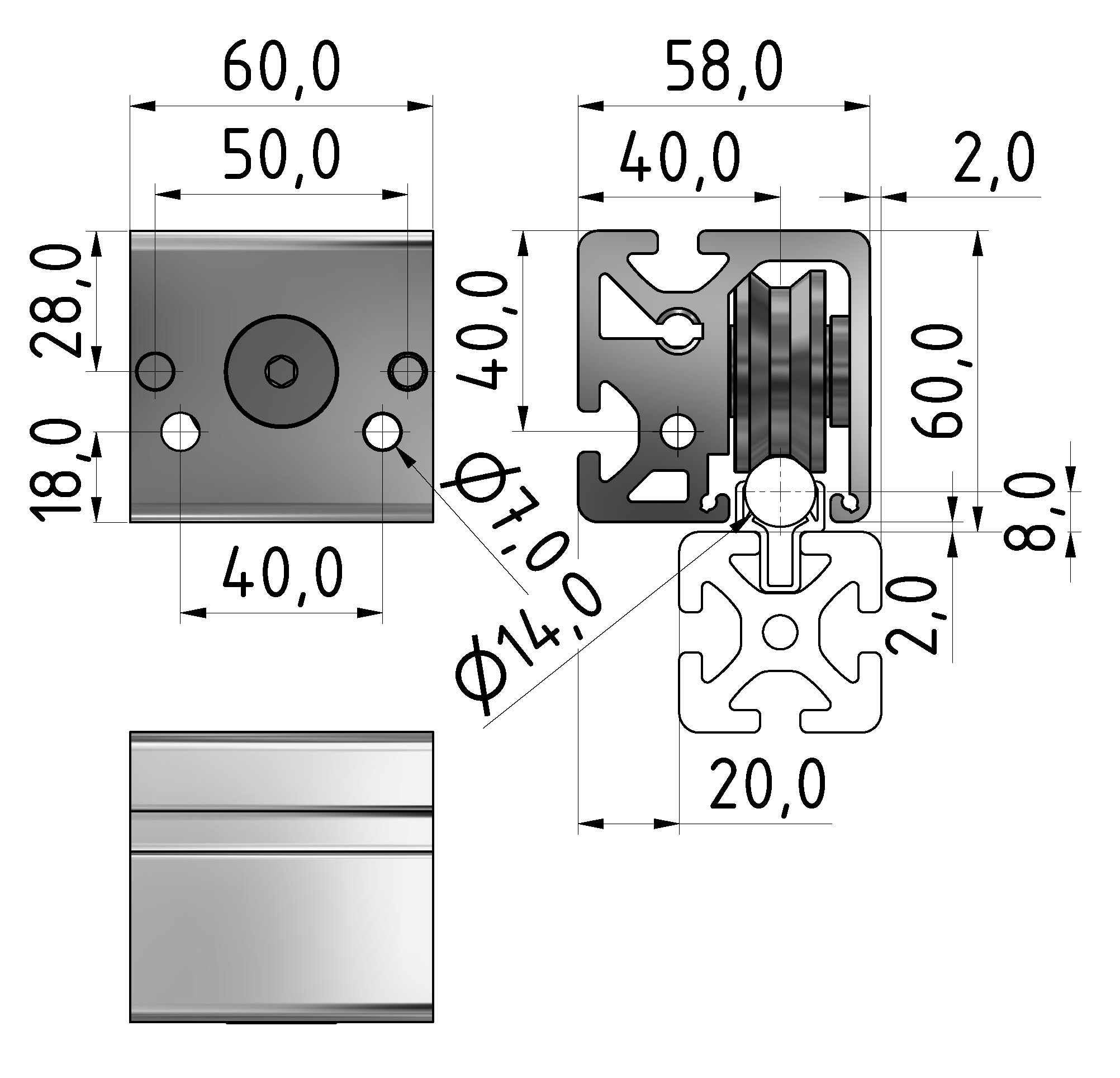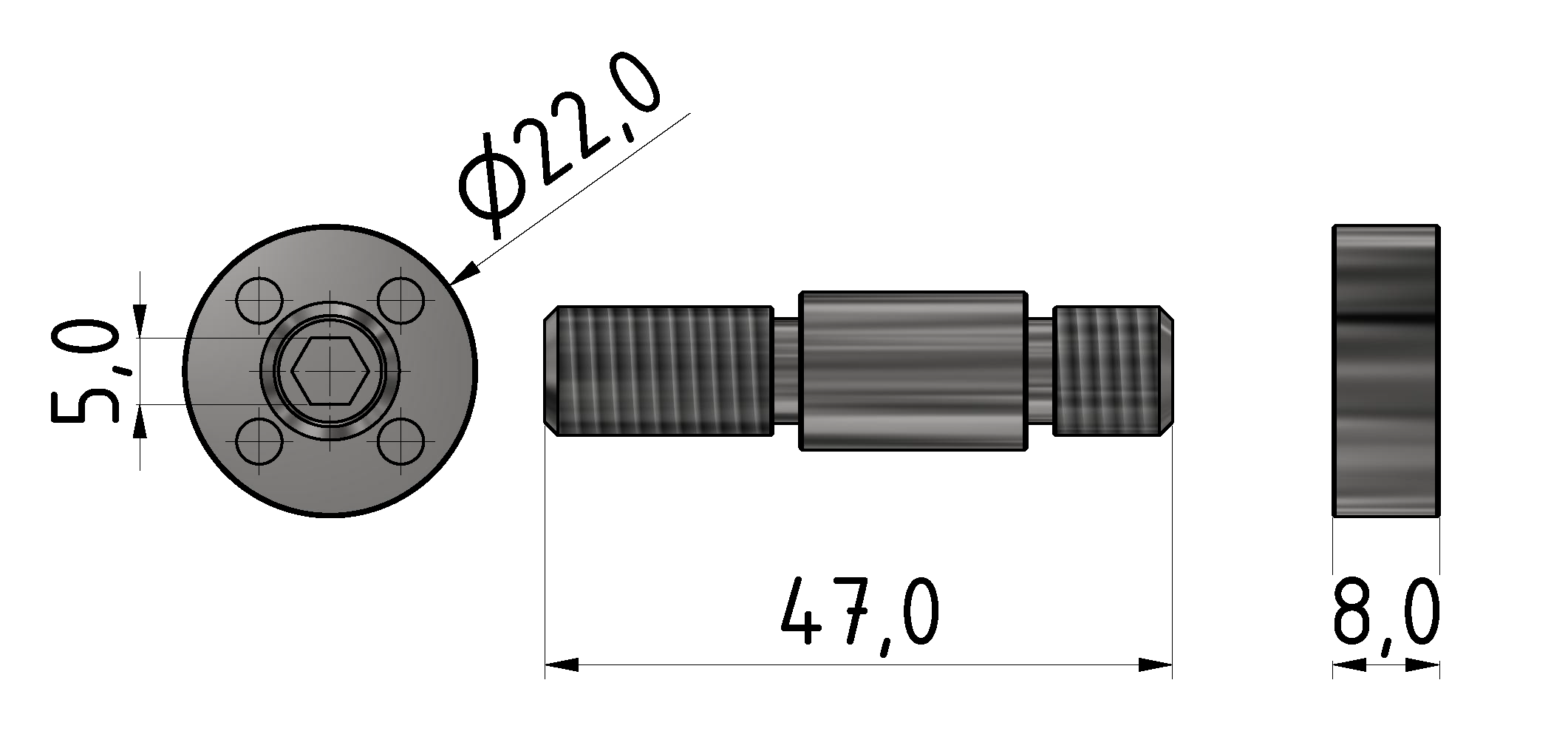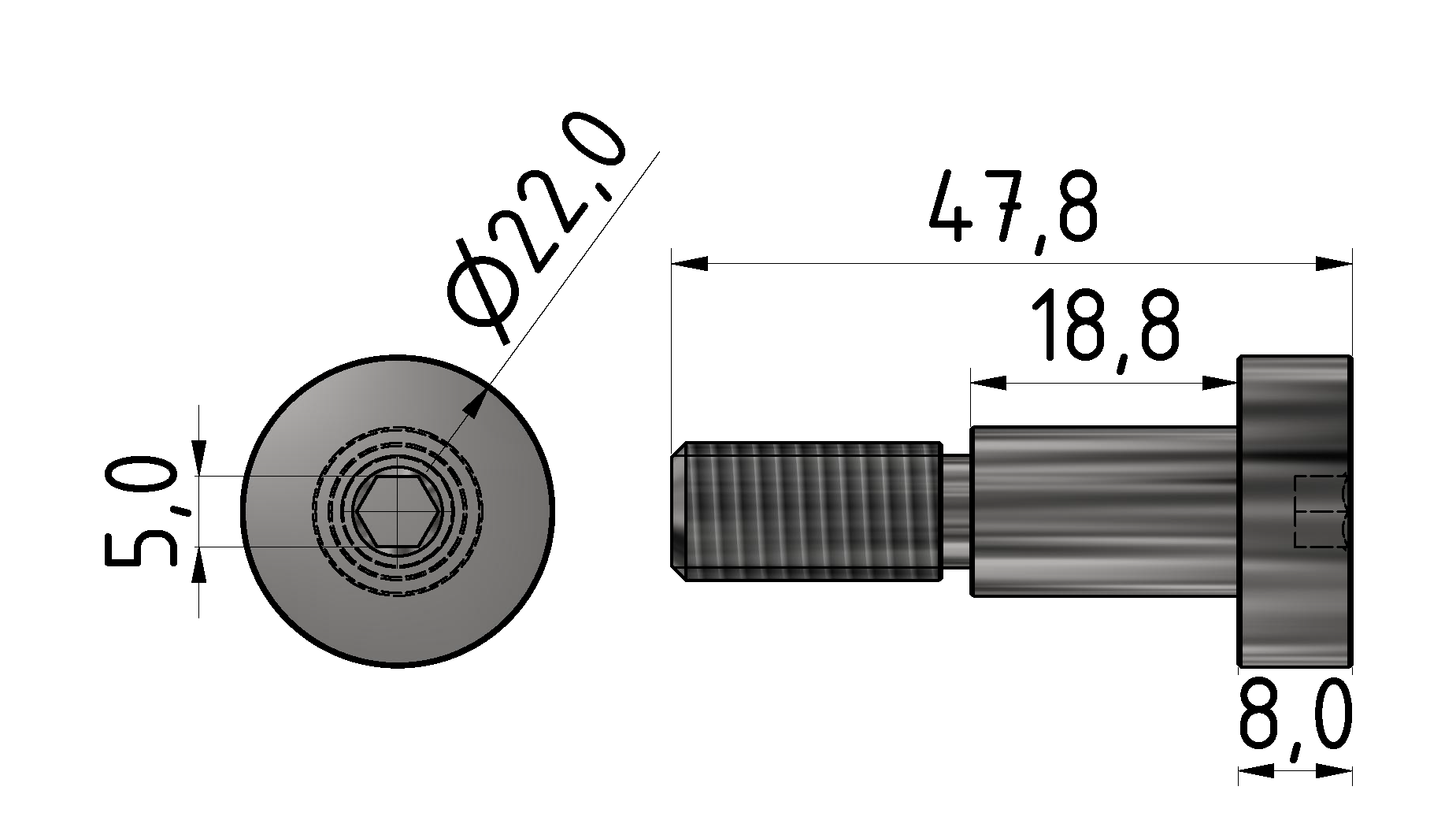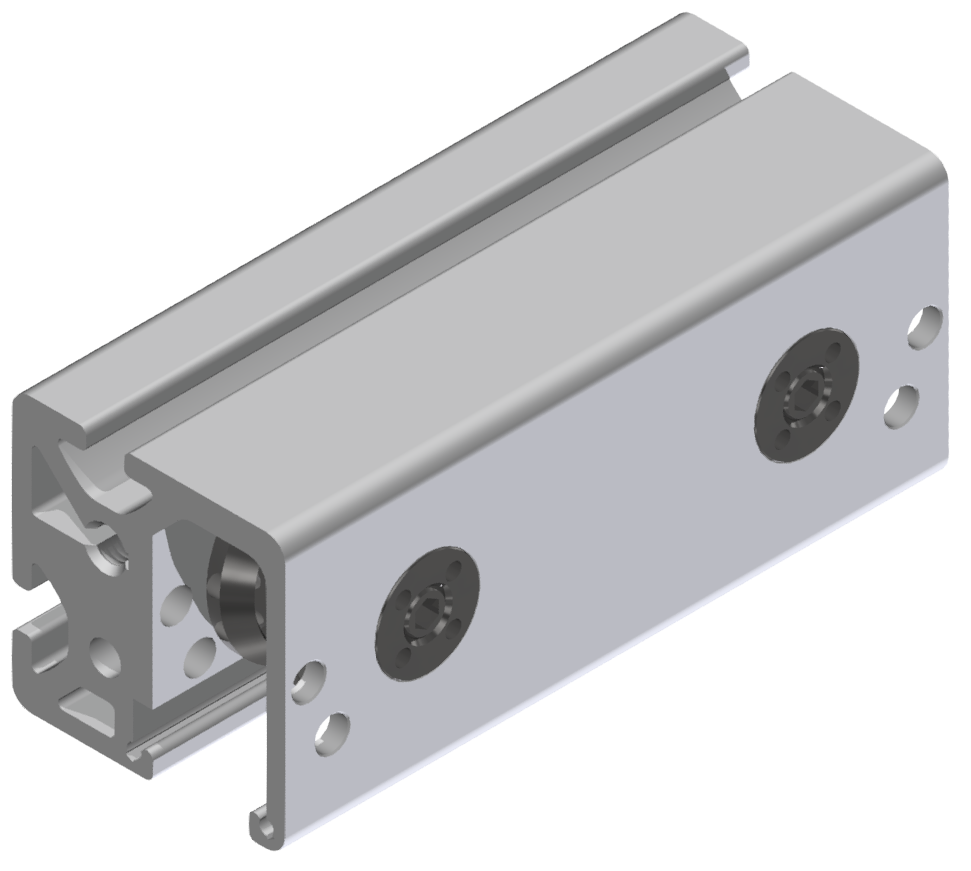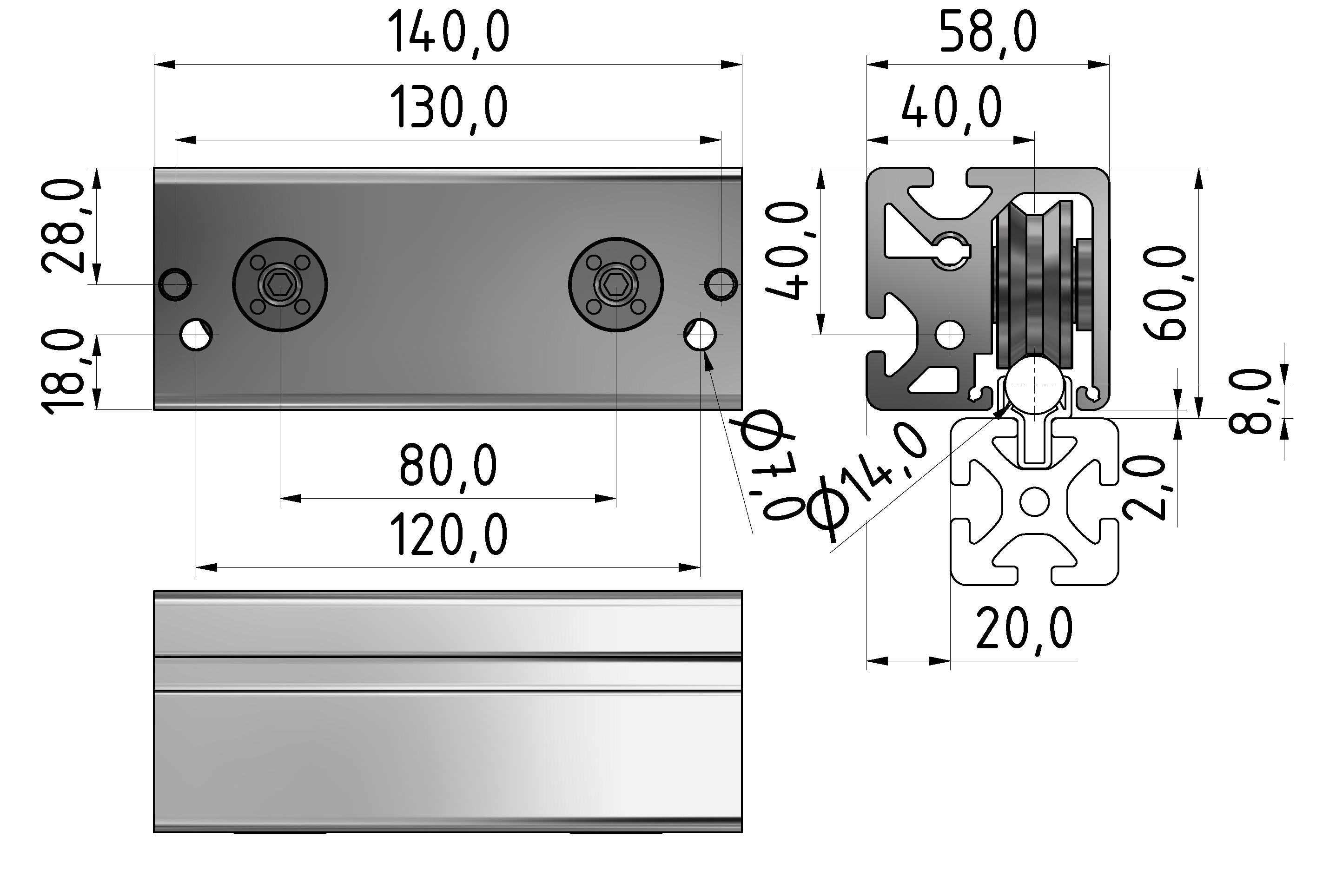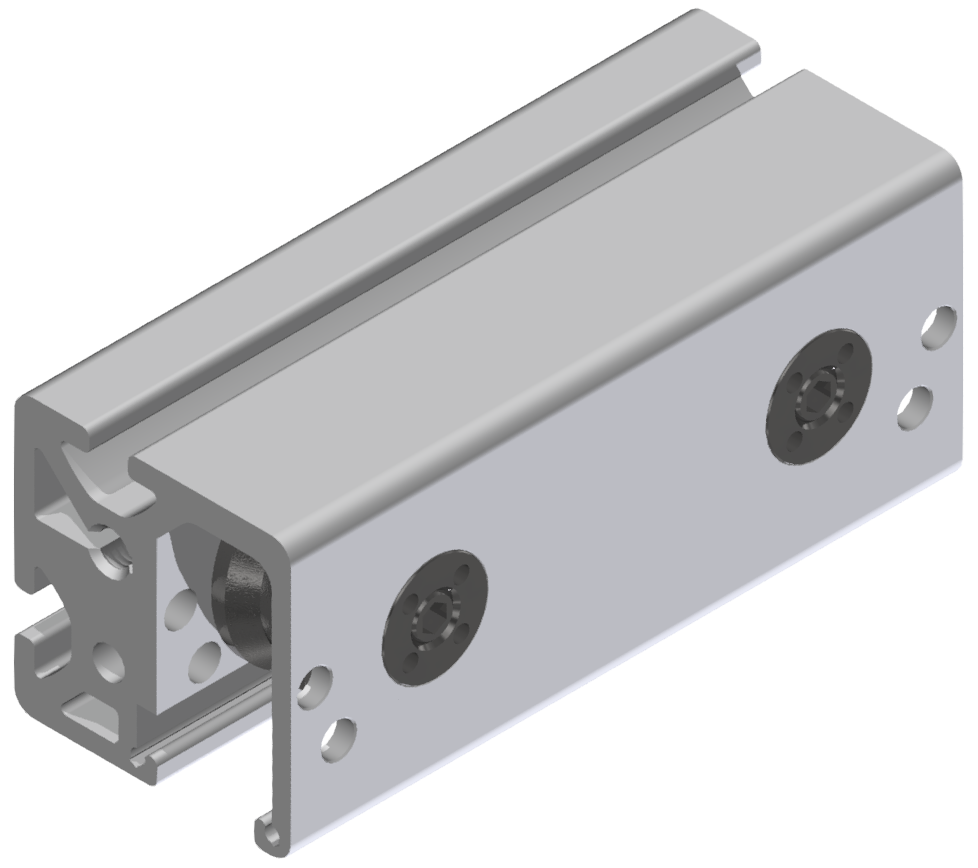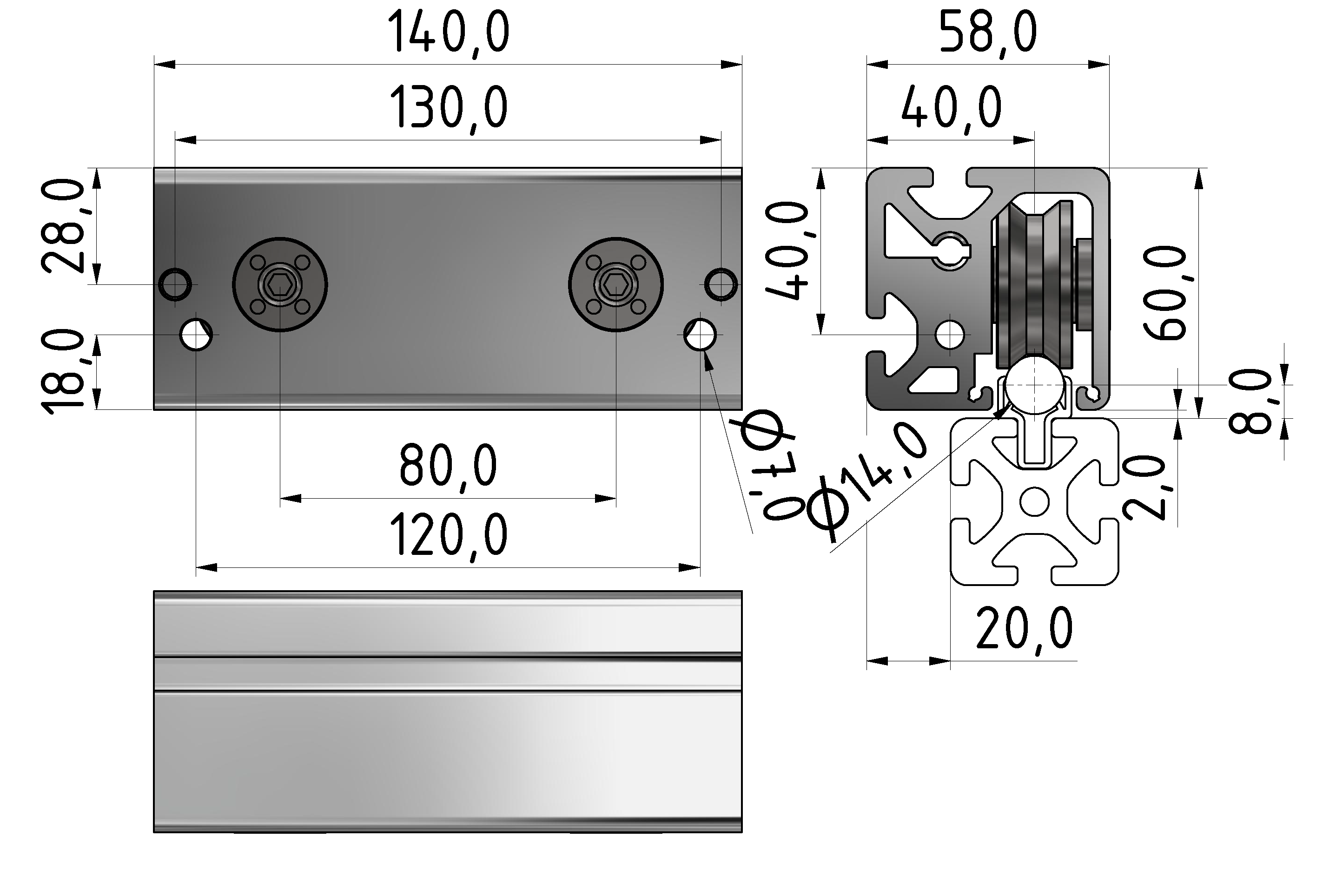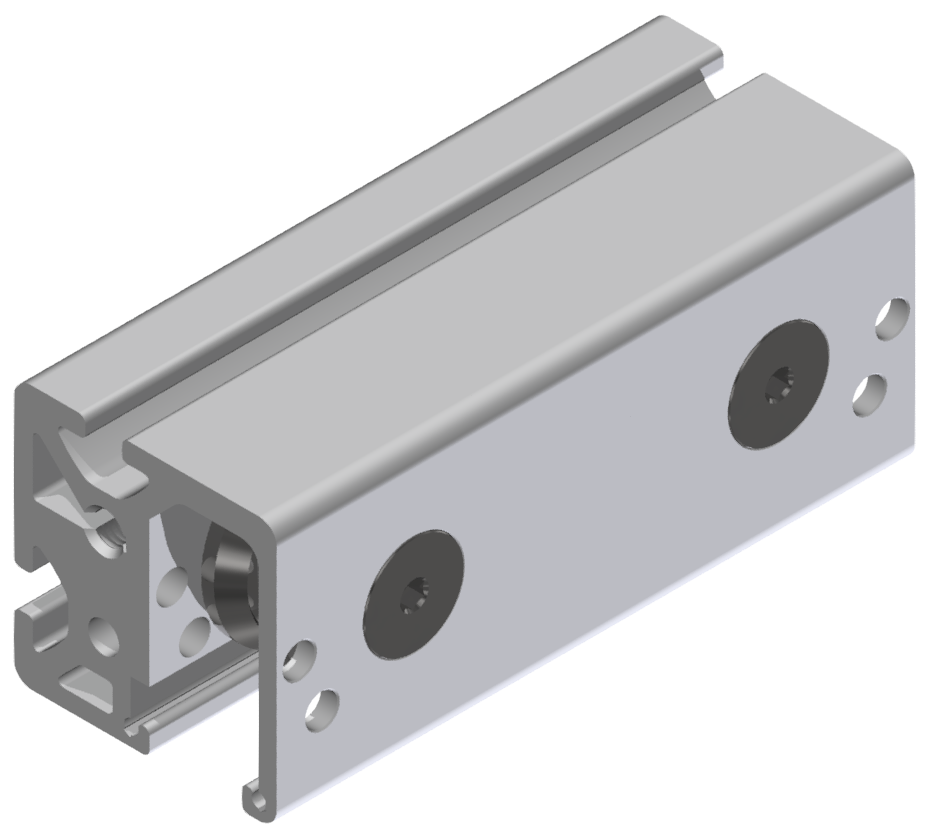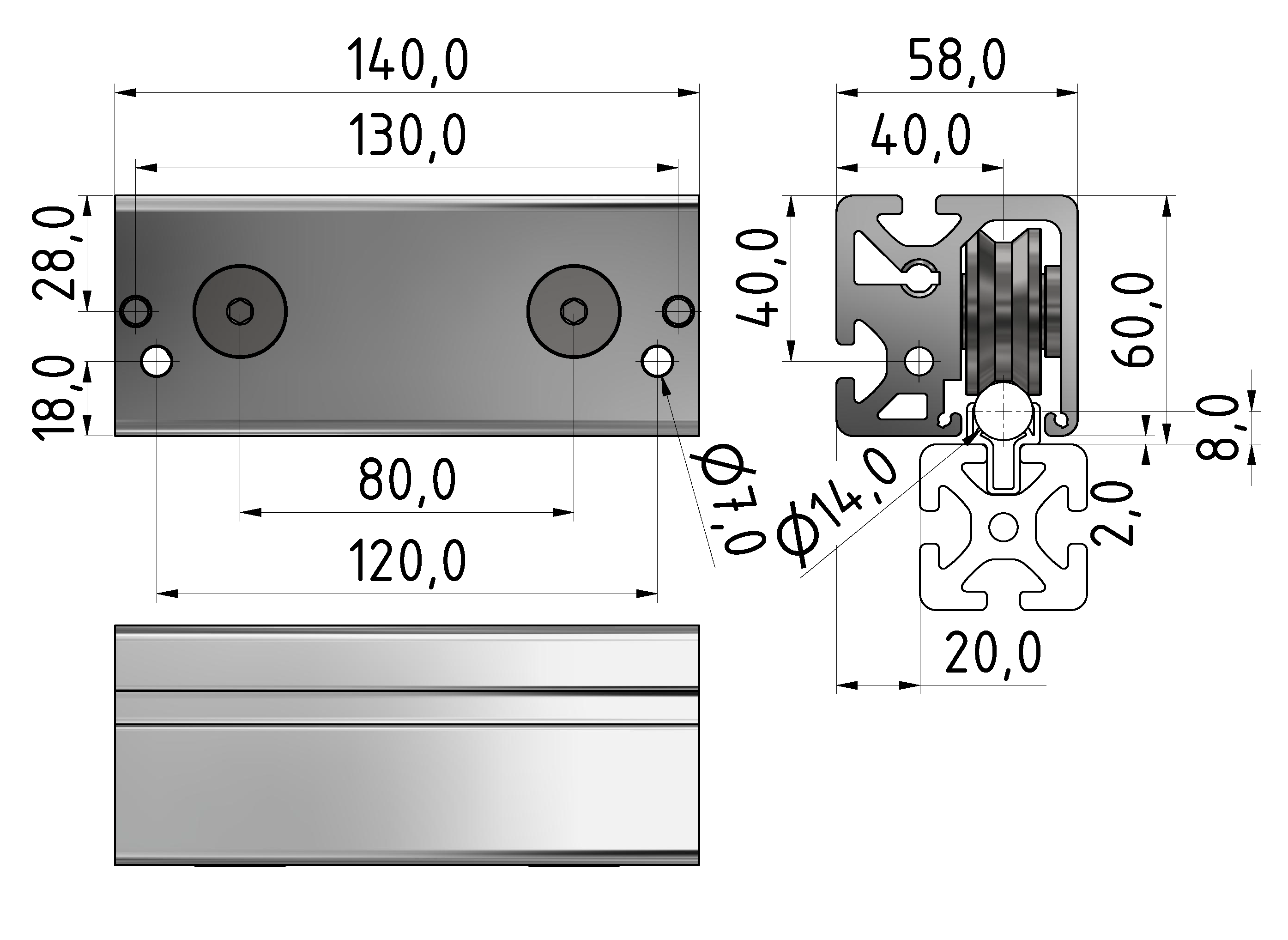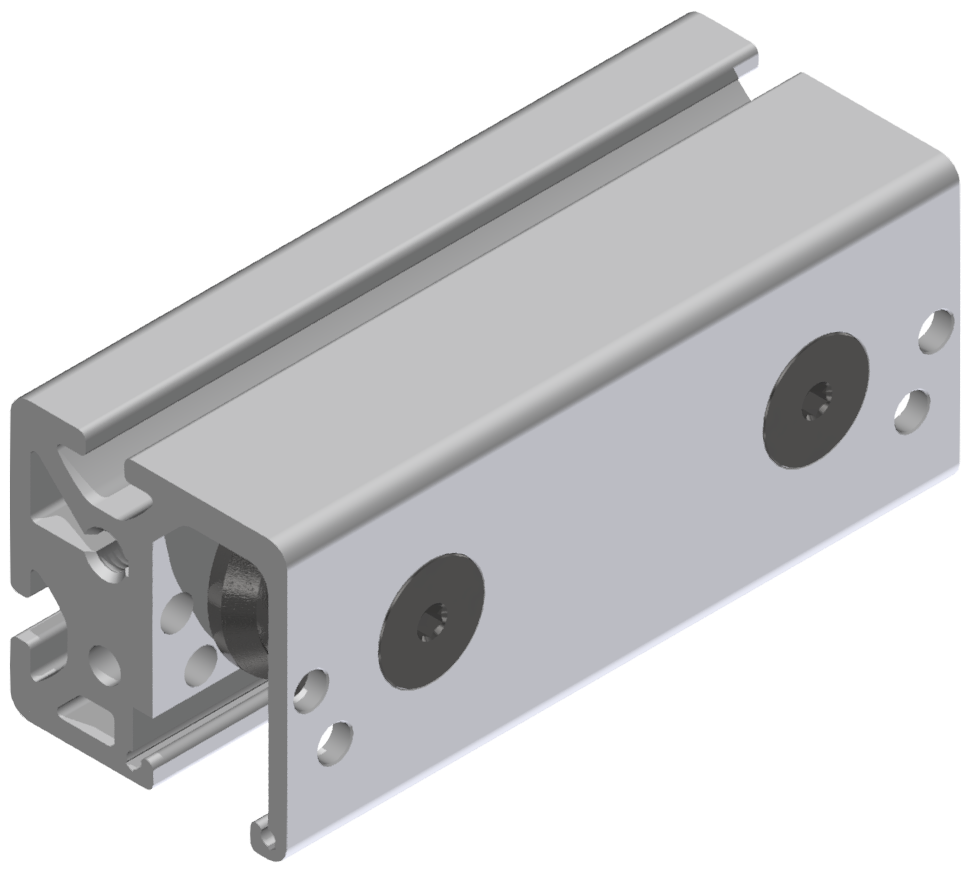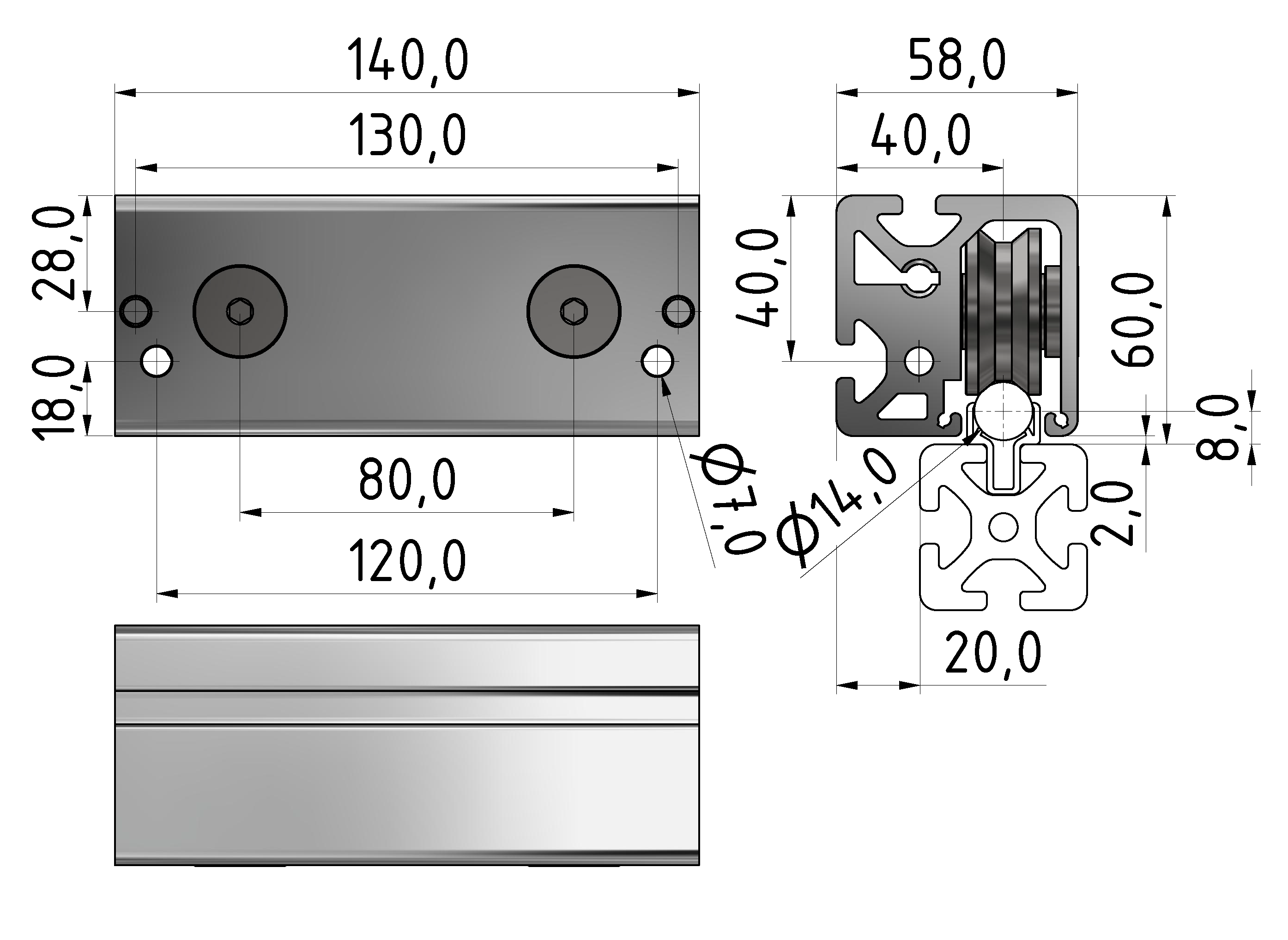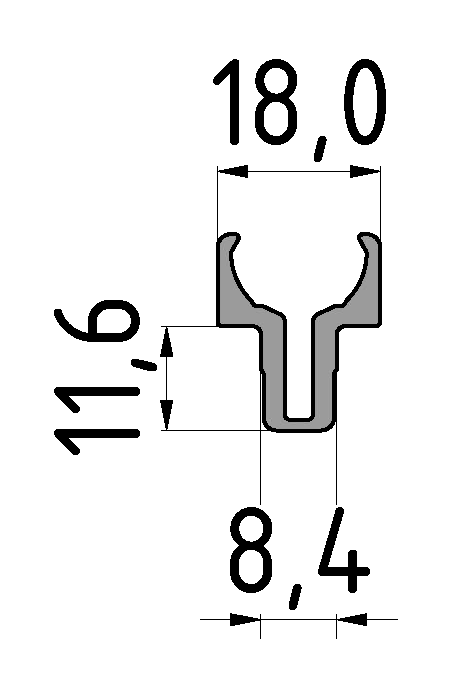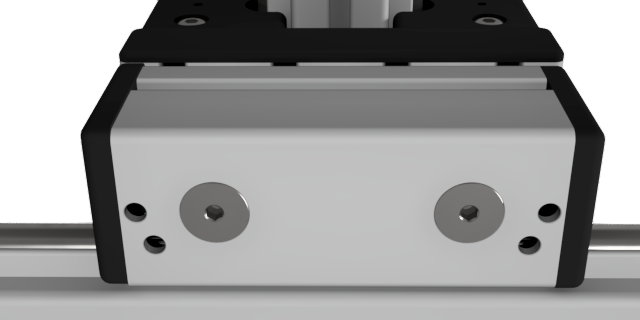
Roller guideways: Precise linear guide systems for demanding applications
Roller guides are indispensable components in linear technology and offer numerous advantages for industrial applications. These robust guide systems are characterized by their high load capacity, precise motion control and long service life.
Roller guides are used in various branches of industry, including:
- Packaging machines
- Automation systems
- Machine safety doors
- Special and rail vehicles
- Medical technology
Features and advantages of roller guides
- High load capacity: Roller guides can handle heavy loads with ease and are ideal for demanding industrial environments.
- Precise motion control: The use of roller chains ensures smooth and stable movement with minimal fluctuations in displacement resistance.
- Dirt resistance: Compared to ball guides, roller guides are significantly less sensitive to contamination, which makes them particularly suitable for harsh environments.
- Low-noise movement: The roller guides generate very little noise, which contributes to a more pleasant working environment.
- Ease of maintenance: Thanks to the use of roller chains and optimized lubricant retention, roller guides enable long-term maintenance-free operation.
FAQ: Frequently asked questions about roller guides
Here you will find answers to frequently asked questions about our roller guides.
What is the difference between roller guides and ball guides?
Roller guides use larger rolling elements (rollers) and are therefore more resistant to dirt and inaccuracies. Ball guides often offer greater precision, but are more sensitive.
What materials are used for roller guides?
Roller guides typically consist of hardened steel rails and steel rollers. Stainless steel or plastic roller versions are also available for special applications.
How are roller guides lubricated?
Many roller guides have integrated lubricant reservoirs for long-lasting lubrication. External lubrication devices can also be fitted.
Can roller guides compensate for misalignment?
Yes, roller guides can compensate for misalignments in the order of millimeters in terms of both parallelism and flatness.